If you want to move money either into or out of your bank account, you’re going to need to know your bank routing number and account number.
A routing number is a nine-digit code used to identify a bank in the United States. It may also be called a Routing Transit Number (“RTN”) or an ABA number (American Bankers Association), they all refer to the same thing.
Banks use routing numbers to direct money to and from one another. So you will need to provide this number when initiating a wire transfer, direct deposit or when setting up automatic bill payments.
Where do you find your Routing Number?
You can typically find the routing number on the bottom left corner of most personal checks. The numbers found at the bottom of a check represent the bank routing number, your specific account number and the individual check number.
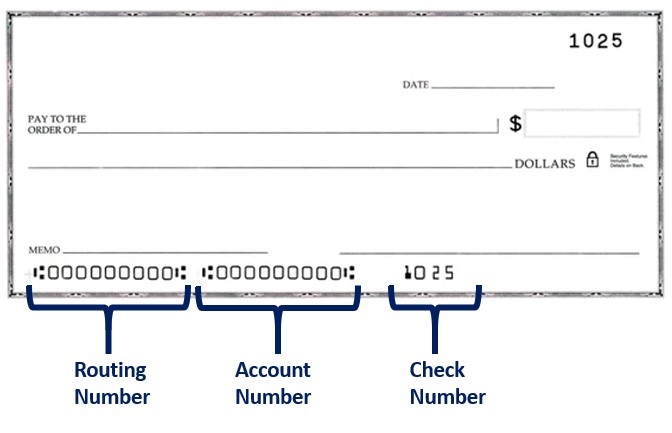
If you don’t have any physical checks to reference, you can also find the ABA number by contacting your bank, checking their website or by logging into your bank’s mobile app.
You could also look up a routing number on the ABA website.
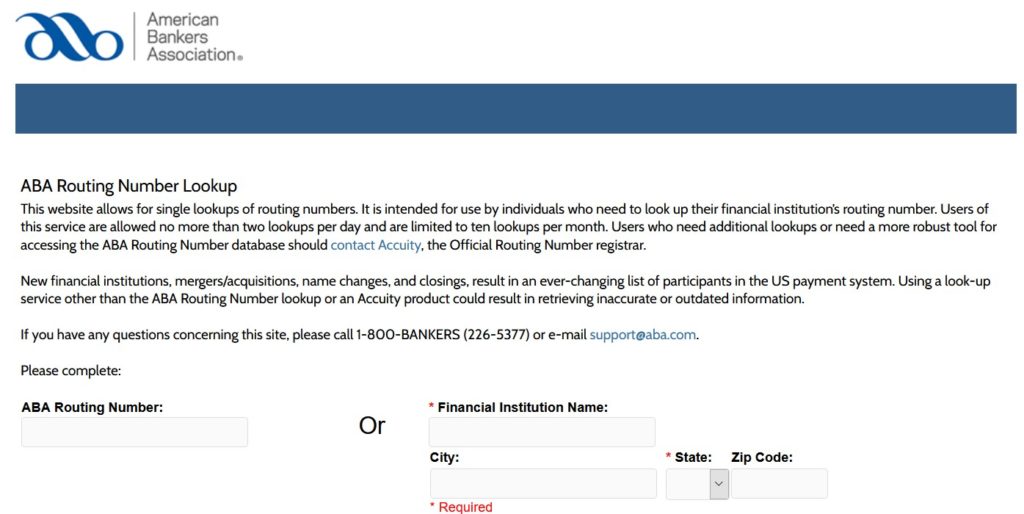
The ABA website’s lookup tool will allow you to find your banks routing number as well as take an existing routing number and find what bank it is associated with.
Routing Number vs. Account Number
Bank transactions require two key pieces of information to identify who you are and what account is yours. The routing number identifies the bank where you have your account and the account number is a 10-12 digit number tha identifies your specific account at that bank.
A smaller bank generally will only have one routing number, while large multinational banks will have many routing numbers, usually based on the state in which you hold the account. So, for example, Chase Bank would have a routing number to identify their banks in the state of Michigan and a different routing number to identify a bank in Ohio.
What is the ABA Number format?
If you really want to dig into the details of a routing number, here is a breakdown what what each of the nine digits in a routing number represents.

- The first four digits represent the city and state of the bank’s location.
- The fifth and sixth digits represent the Federal Reserve bank that the institution’s electronic and wire transfers will route through.
- The seventh digit indicates which Federal Reserve check processing center was assigned to the bank.
- The eighth digit represents the Federal Reserve district the bank is in.
- The ninth digit provides a checksum. The checksum is a complicated calculation to make sure the routing number is valid.
Who Issues ABA Numbers?
Routing numbers can only be issued to a bank by a company called Accuity, which serves as the official routing number registrar for the American Bankers Association, or ABA.
In order to apply for a routing number, a financial institution must submit the following to the Registrar:
- Completed Application and Agreement
- Preliminary, or final, charter approval from the chartering agency (State Banking Department, OCC, NCUA etc.)
- The application fee: see application for fees.
ABA Routing Numbers for Some of the Largest Banks
Here is where to find the routing number for a handful of the largest banks in the United States.


 Chase Credit Journey Review: How to Check Your Score For Free
Chase Credit Journey Review: How to Check Your Score For Free